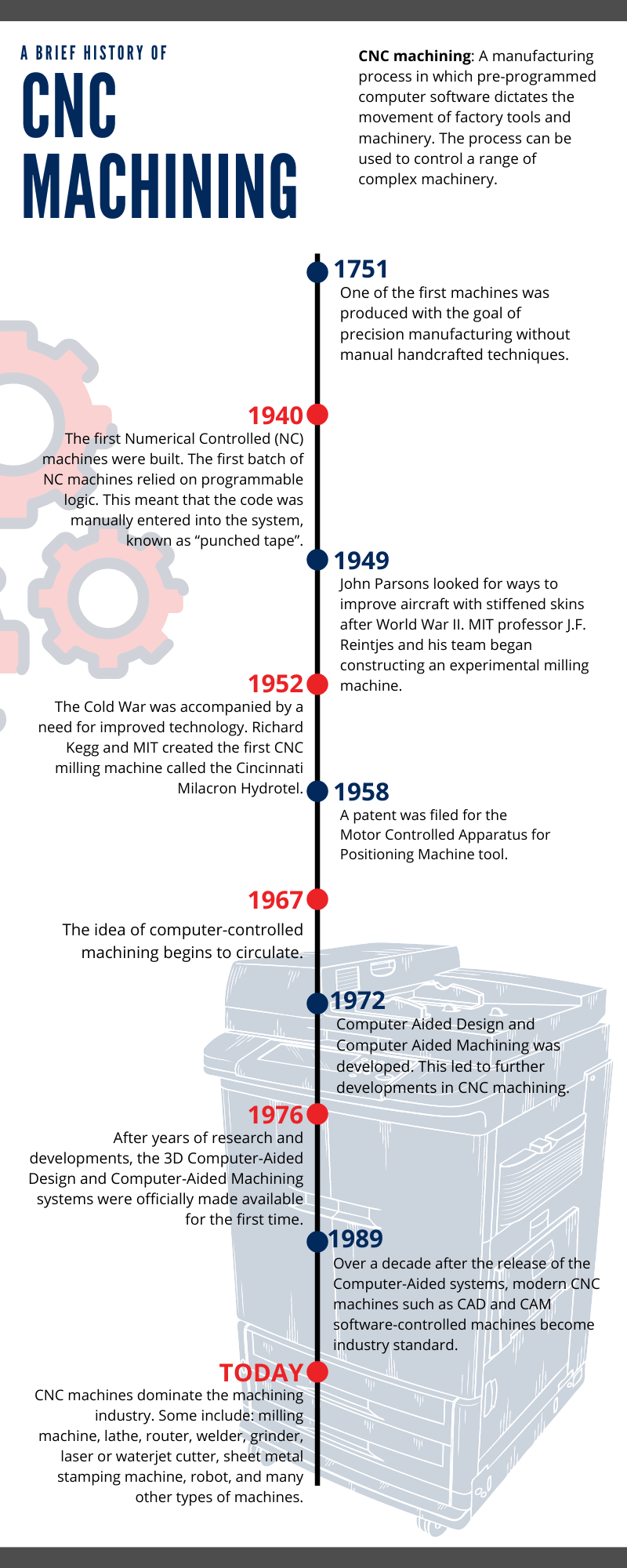
Welcome to the World of CNC Machining

Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. This technology, which automates the manufacturing process using computerized controls and machinery, has its roots in the 1940s and 1950s and has since become an indispensable asset across various sectors.
The Evolution of CNC Machining
CNC technology gained traction in China during the 1980s and 1990s, and the country has since become a global leader in CNC machining and manufacturing. China's investment in state-of-the-art facilities and skilled personnel has positioned it as a hub for high-precision manufacturing.
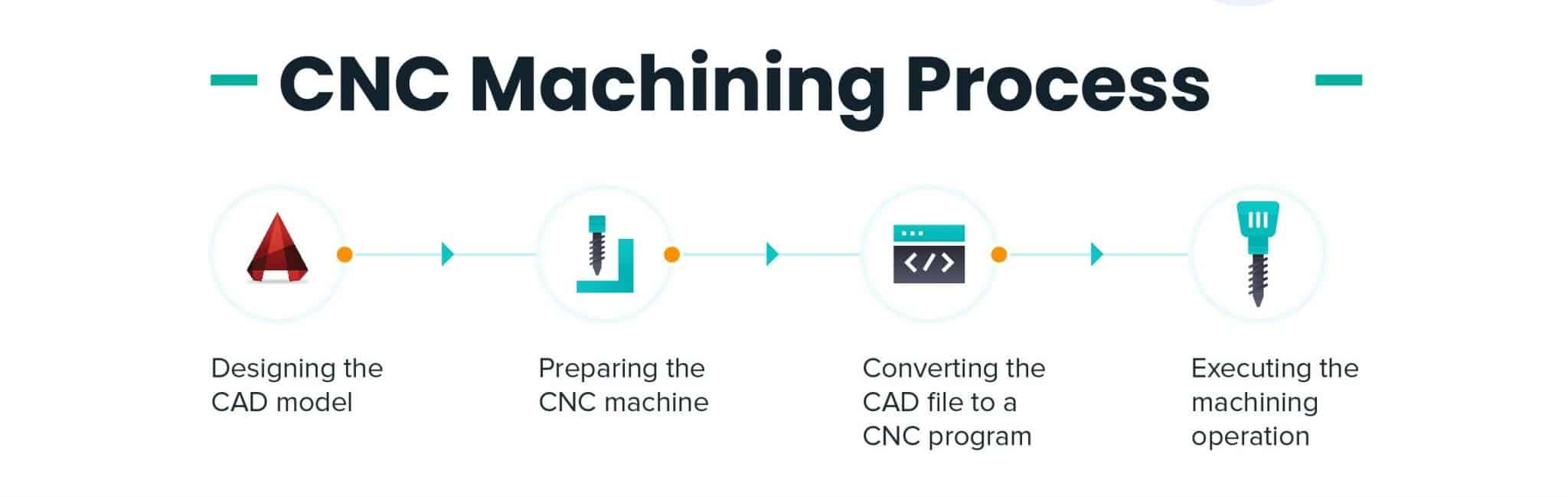
Production Processes
CNC machining involves a series of automated steps from raw material to finished product:
Material Selection and Preparation: The choice of material is critical, with properties like hardness and machinability determining the approach to machining
Programming: CAD software and CAM software are used to design the part and generate machine instructions in G code
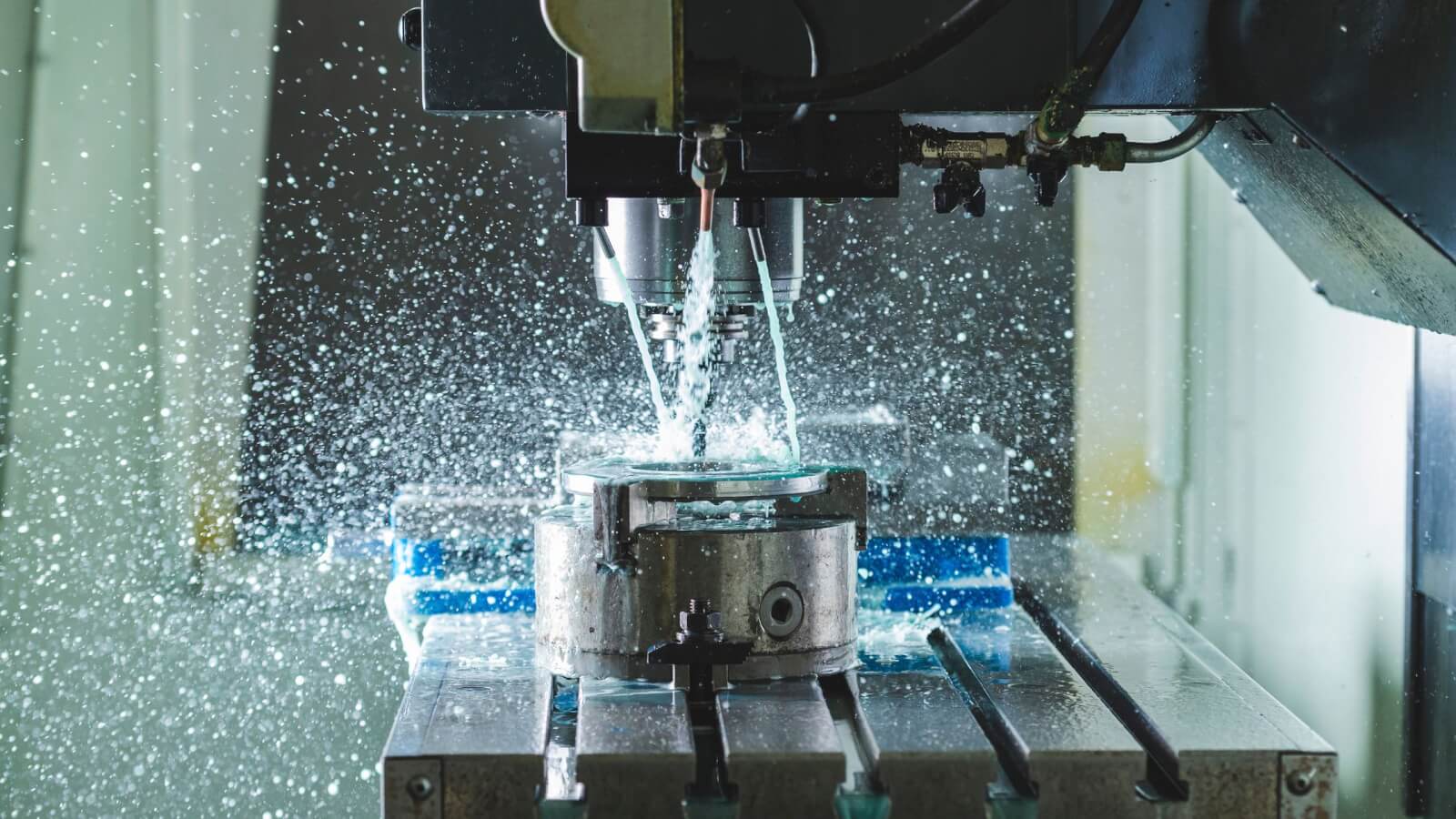
Machining Operation: CNC machine tools such as mills, lathes, and routers carry out operations based on the programmed instructions
Inspection and Quality Assurance: Regular inspections ensure parts meet stringent quality standards, using techniques like CMM and automated visual inspection
Post-Processing: Parts may undergo treatments like heat treatments, anodizing, or painting to enhance strength, durability, or aesthetics
Final Inspection and Shipping:Finished parts are inspected to ensure they meet all specifications before packaging and shipping
Classifications and Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines used in production include mills, lathes, routers, and are essential in high-volume manufacturing environments .
Materials for CNC Machining
The versatility of CNC machining allows compatibility with a broad spectrum of materials:
1.Metals: Commonly used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical applications. Steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and titanium are all machinable metals .
2.Plastics: Used in refrigeration components, electronics, toys, and sports industries. Acrylic, polycarbonate, PVC, and nylon are commonly machined plastics .
3.Ceramics: Used in advanced applications like space shuttle engine components and tank armor .
4.Composites: Require diamond tooling and 5-axis CNC machines, used in automotive, aerospace, and power generation industries .
5.Wood: Limited to artistic applications like furniture and decoration, and some structural applications .
Surface Treatments
Surface treatments are crucial for improving the longevity and functionality of CNC-machined parts:
1.Grinding: Uses an abrasive wheel to provide a uniform and smoother finish .
2.Chemical Finishing Methods: Include passivation, chemical conversion coating, galvanizing, black oxide coating, and vapor polishing .
3.Electrical/Electrochemical Finishing Methods: Such as anodizing, electroplating, electroless nickel plating, electropolishing, and powder coating .
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely used across various industries:
1.Automotive: Engine parts, gearbox cases, suspension components, and intricate car body parts .
2.Medical: Surgical tools, orthopedic implants, MRI scanners, and imaging equipment components .
3.Electronics: Circuit boards, enclosures, heat sinks, and RF components .
4.Military and Defense: Weapon components, communication equipment parts, and vehicle components .
5.Oil and Gas: Drilling tools, valves, and pipe fittings .
6.Renewable Energy: Wind turbine blades, solar panel frames, and hydroelectric turbine components .
Market Prospects
The global CNC machine market is projected to grow from USD 83,676.1 Billion in 2024 to USD 1,23,627.6 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.0% during the forecast period (2024 - 2032). The demand for CNC machines from various industries and evolving advanced technology are key market drivers enhancing the growth of the market .
This introduction provides a comprehensive overview of the CNC machining industry, covering its processes, classifications, materials, surface treatments, applications, and market prospects.




